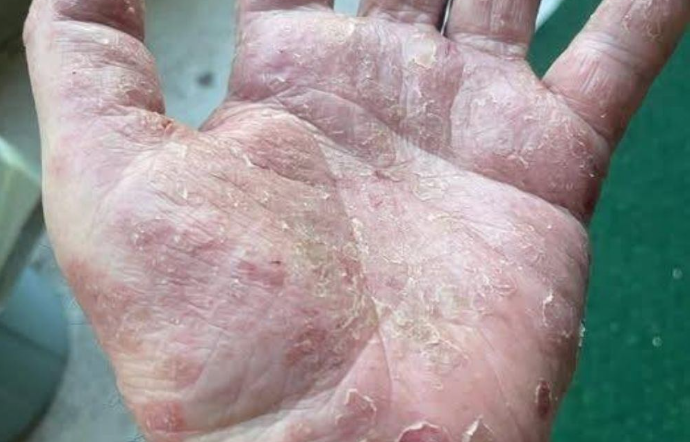
Hand dermatitis, commonly referred to as hand eczema, is a prevalent skin condition that impacts countless individuals worldwide, often causing significant discomfort. The image provided illustrates a hand with visible redness, peeling, and irritation—hallmark indicators of acute hand dermatitis. While some experience mild, temporary symptoms, others face chronic issues, leading to ongoing pain, self-consciousness, and challenges with routine activities.
Gaining insight into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effectively controlling this condition.
What Triggers Hand Dermatitis?
Hand dermatitis arises from a combination of factors rather than a single source. These influences often include environmental, genetic, and lifestyle elements. Common contributors include:
Harsh chemicals in soaps, detergents, or disinfectants that remove the skin’s natural protective oils, leaving it dry and prone to irritation.
Frequent water exposure, particularly for professionals like healthcare workers, cleaners, hairstylists, or chefs who wash their hands repeatedly, compromising the skin’s protective barrier.
Allergic responses to substances such as nickel, latex, or fragrances found in cosmetics and skincare products.
Pre-existing conditions, like atopic eczema or psoriasis, which increase the likelihood of developing chronic hand dermatitis.
Environmental conditions, where cold, dry climates can intensify symptoms, while humid environments may extend flare-ups.
Identifying the Symptoms
The severity of hand dermatitis symptoms varies, but common signs include:
Red, inflamed, and warm skin that feels irritated.
Dry, flaky, or peeling skin as the outer layer deteriorates.
Painful fissures or sores that may bleed.
Persistent itching or burning sensations that interfere with sleep or daily tasks.
Thickened, rough skin in cases that persist over time.
If left untreated, the condition may escalate, potentially leading to infections. Look for warning signs like pus, swelling, or intense tenderness.
Effective Treatment Strategies
Managing hand dermatitis typically involves a blend of medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments. Key approaches include:
Regular moisturizing with thick, fragrance-free creams or ointments applied multiple times daily to hydrate and reinforce the skin’s barrier.
Protective gloves when handling cleaning products, washing dishes, or using chemicals. Pairing rubber gloves with cotton liners can minimize sweat accumulation.
Gentle cleansers that are soap-free to replace harsh antibacterial soaps. Thoroughly dry hands and apply moisturizer immediately after washing.
Prescription treatments, such as corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation or calcineurin inhibitors for more severe cases.
Advanced therapies, like light therapy or oral medications, which dermatologists may recommend for persistent or severe cases.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
Mild cases may respond to self-care, but professional evaluation is crucial if:
The condition hinders daily tasks or routines.
Painful cracks, bleeding, or open sores appear.
Over-the-counter treatments fail to provide relief.
Signs of infection, such as pus or significant swelling, develop.
A dermatologist may perform patch testing to identify specific allergens and create a personalized treatment plan.
Closing Thoughts
Though hand dermatitis may appear to be a minor issue, it can profoundly disrupt daily life. Routine activities like cooking, typing, or even shaking hands may become painful or uncomfortable. Fortunately, with appropriate treatment and proactive care, many individuals can successfully manage flare-ups and safeguard their skin from long-term damage.