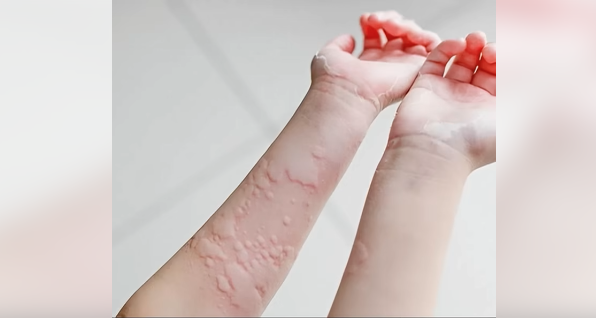
You awaken to find red, itchy welts scattered across your arms, legs, or torso.
They flare up, itch intensely, and spread rapidly — only to fade away as quickly as they appeared.
You might suspect an allergy to something you ate or a new soap you tried — but could the true culprit be something entirely unexpected?
Hives, also known as urticaria, impact up to 20% of people at some point in their lives. While some cases stem from familiar triggers like peanuts or insect stings, many are sparked by less obvious, often overlooked causes that remain hidden in plain sight.
Let’s explore the unexpected triggers of hives — empowering you to recognize, avoid, and manage them effectively.
🧪 Understanding Hives
Hives are raised, red, itchy patches or bumps that form when mast cells in the skin release histamine, a chemical tied to allergic and immune responses.
They can manifest as:
Acute: Lasting less than 6 weeks.
Chronic: Persisting beyond 6 weeks, often without an identifiable cause.
Though typically harmless, hives can be uncomfortable, distressing, and disruptive to daily life.
🔍 Familiar Triggers You Likely Recognize
- 🥜 Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs)
- 💉 Insect bites or stings
- 🌼 Pollen or pet dander
- 🧴 Medications like antibiotics or NSAIDs
- 🧼 Fragranced soaps or lotions
But what about the triggers that catch you off guard?
🚨 7 Unexpected Causes of Hives You Might Overlook
1. 🔥 Heat, Sweat, and Exercise (Cholinergic Urticaria)
- Caused by an increase in body temperature, not allergens.
- Often triggered by workouts, hot showers, or stressful moments.
- Small, intensely itchy welts appear within minutes.
✅ Tip: Opt for breathable fabrics and cool down slowly after physical activity.
2. ❄️ Cold Exposure (Cold Urticaria)
- Hives emerge after contact with cold air, water, or ice.
- Can even occur after sipping a chilled beverage.
- In rare cases, may cause swelling or severe allergic reactions.
✅ Tip: Limit exposure to cold and keep antihistamines on hand if diagnosed.
3. 👔 Pressure or Tight Clothing (Delayed Pressure Urticaria)
- Deep, painful hives result from tight belts, straps, or prolonged sitting.
- Welts may appear 4–6 hours after pressure is applied.
- Common in those with chronic hives.
✅ Tip: Choose loose-fitting clothing and avoid extended pressure on the skin.
4. 🦠 Infections (Particularly Viral)
- Conditions like the common cold, strep throat, urinary tract infections, or even COVID-19 can prompt hives.
- More frequent in children.
- Hives may appear before other symptoms surface.
✅ Note: The immune system’s reaction — not the infection itself — triggers the hives.
5. 💊 Medications You Might Not Suspect
- Beyond antibiotics, drugs like aspirin, ibuprofen, blood pressure medications, or even certain vitamins can cause hives.
- Reactions may be delayed, appearing days after starting a new medication.
✅ Tip: Inform your doctor about all medications when hives occur.
6. 🧬 Autoimmune Conditions
- Chronic hives are often associated with autoimmune disorders, such as:
- Lupus
- Thyroid conditions (e.g., Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- The body mistakenly attacks its own tissues, including skin cells.
✅ Tip: If hives persist beyond 6 weeks, request thyroid or autoimmune testing from your doctor.
7. 🍽️ Food Additives and Preservatives
- The issue may not be the food itself, but its additives:
- Artificial colors (e.g., Red 40, Yellow 5)
- Preservatives (e.g., sulfites, benzoates)
- Flavor enhancers (e.g., MSG)
- Common in processed snacks, sodas, and fast food.
✅ Tip: Consider an elimination diet with guidance from a healthcare professional.
🧪 When to Seek Medical Advice
Most hives resolve on their own, but consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Hives lasting more than 6 weeks (chronic urticaria).
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema).
- Difficulty breathing or dizziness — seek emergency care immediately.
- Recurrent hives with no apparent cause.
🩺 Next Steps: A dermatologist or allergist can pinpoint triggers through skin tests, blood work, or elimination diets.
✅ Strategies to Manage Hives
- Identify the Trigger: Pinpoint and avoid the cause.
- Use Antihistamines: Try over-the-counter options like cetirizine or loratadine.
- Soothe the Skin: Apply a cold compress or take an oatmeal bath.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Minimize irritation from tight fabrics.
- Track Symptoms: Keep a diary of food, activities, and flare-ups.
❌ Avoid Scratching: Scratching intensifies inflammation and risks infection.
Final Thoughts
Hives aren’t always tied to allergies.
Sometimes, the true cause is right in front of you — hidden in your exercise routine, medication list, or even your go-to snack.
By uncovering these surprising triggers, you can take charge of your skin’s health and reclaim your comfort.
The next time that familiar itch strikes, don’t only treat the welts.
Dig deeper to uncover the cause.
Because with hives, the answer is often more unexpected than you might imagine.